L.L. Vasiliev, O.S. Filatova, A.P. Tsitovich
Luikov Heat and Mass Transfer Institute, National Academy of Sciences, Belarus, Leonard_Vasiliev@rambler.ru
ABSTRACT: In the 21st century the way to increase the efficiency of new sources of energy is directly related with extended exploration of renewable energy. This modern tendency ensures the fuel economy needs to be realized with nature protection. The increasing of new power sources efficiency (cogeneration, trigeneration systems, fuel cells, photovoltaic systems) can be performed with the help of solid sorption heat pumps, regrigerators, accumulators of the heat and cold, heat transformers, natural and hydrogen storage systems and efficient heat exchangers.
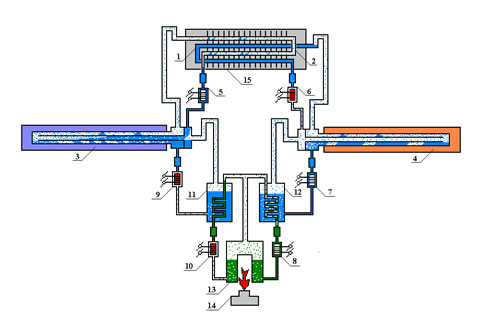
Two stage solid sorption heat pump with complex compound sorbent bed inside (combination with solid sorption stage (adsorption) and liquid sorption stage (absorption)): 1, 2 – low temperature heat exchangers; 3, 4 – high temperature adsorbers filled with "Busofit"+NiCl2 micro crystals, fluid is ammonia; 5–10 – valves; 11, 12 – heat pipe based heat exchangers; 13 – mini-boiler; 14 – gas flame; 15 – LiBr/water low temperature absorber with heat recovery by heat pipes
New power sources efficiency (co-generation, tri-generation systems, fuel cells, photovoltaic systems) have a good perspective to be increased combined with the renewable energy resources through solid sorption heat pumps, regrigerators, accumulators of the heat and cold, heat transformers, natural and hydrogen storage systems.
The developed and tested experimental set-up offers the possibility of saving 15–20% of primary energy for cooling, heating and power demands.
The additional experiments with set-up based on the coupling salts NiCl2, MnCl2, BaCl2 with an active carbon fibre "Busofit" have demonstrated a possibility to have a cooler with two different independent sources of cold (low temperature BaCl2 adsorber and evaporator) with simultaneous heat generation and chilled water production with COPcooling equal 0.6 and the heat pump COP near 1.6.